Results of WT DNA through gel electrphoresis
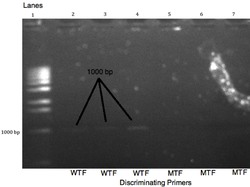
The results from amplified products using gel electrophoresis. The non-discriminating oligonucleotide reverse primer, R, is 2% 3’-GTGGCTGCAGGGTTACAACTA-5’. The discriminating oligonucleotide forward primer CDF is 2% 5’-CGGGACGAGGCCGCG-3’. The discriminating oligonucleotide forward primer WTF is 2%5’-GCGGGACGAGACCGCG-3’. The binding site is on chromosome 16 on the CARD 15 gene from position 19,866 b.p. to 19,881 b.p. for the forward primer CDF, from position 19,866 b.p. to 19,881 b.p. for the forward primer WTF, and from position 20,866 b.p. to 20,887 b.p. for the reverse primer R with respect to the CARD 15 gene. There was a yield of 1.7 billion copies of the target DNA, along with a negligible amount of much larger DNA fragments (a by-product of PCR), and the original DNA template. The denaturing temperature was set at 95°C, the annealing temperature at 54°C, and the extension temperature at 72°C. An initial denaturing time of five minutes was used, then the times were 30 seconds denaturing, 45 seconds annealing, 45 seconds extending, and a final extension of 7 minutes for 35 cycles. The agarose gel contains 10% agarose. The wild-type bands were predicted to appear at 1021 base pairs and are shown at roughly the 1000 base pairs and the absence of band in the mutant wells denote that the DNA is, in fact, homozygous wild-type DNA. Bromphenol blue dye will be added to the gel to indicate when the gel electrophoresis is complete. Lane 1 contains the molecular marker or ladder, and lanes 2,3,4,5,6, and 7 contains 2% DNA purified products from wild-type DNA template. The wild-type forward primer is in lanes 2,3, and 4 while the mutant-type primer is in lanes 5,6, and 7. Lane 8 has the control, where no primers were added.
PCR
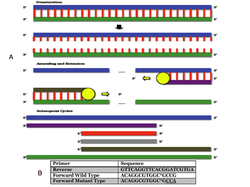
(A) In the denaturation step, the sense strand (blue) and the antisense strand (green) are shown connected by red lines. These red lines represent hydrogen bonds between complimentary nuleotide bases of cytosine, guanine, adenine, or thymine. The large blue and green lines are phosphate-deoxyribose backbones. Together, the two backbones and their bonded bases form DNA template. When temperatures are hot enough (black arrow), the bonds between nucleotide bases are broken. This is the process known as denaturation. During annealing, oligonucleotide primers will bind to the DNA templates. A reverse primer (purple) binds to the sense strand and a forward primer (brown) binds to the antisense strand. During extension, taq polymerase will always extend the primers toward the 3’ end by grabbing dNTPs out of the solution. As a result, and antisense (grey) and sense (red) target area will begin to amplify much faster than the products of other sizes, and after around 20-30 cycles the medium (purple and brown) and large (blue and green) products will be negligible compared to the amount of small red and grey product. Because the position of the primers is known, so is the size of the expected product. This process is used to amplify the R702W mutation in our experiments.
(b) Primers were designed to anneal to the human CARD15 gene at the 702 codon. The underlined codon was changed to anneal to the mutant type. The asterisked base pair was an intentional mismatch included in both primers. Approximately 1000 base pairs were between the forward and reverse primers.
(b) Primers were designed to anneal to the human CARD15 gene at the 702 codon. The underlined codon was changed to anneal to the mutant type. The asterisked base pair was an intentional mismatch included in both primers. Approximately 1000 base pairs were between the forward and reverse primers.
Paneth Cells
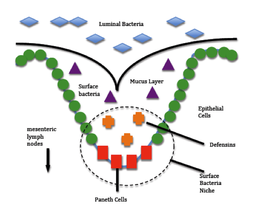
Visual representation of the role of paneth cells in Crohn’s disease. R702W causes an overproduction of defensins in paneth cells in the colon resulting in an autoimmune response, in which epithelial cells are attacked by the immune system of the body causing severe inflammation. Surface bacteria (purple) are different from luminal bacteria (blue) because they can live in the mucus layer. The small crevices in the epithelial lining of the colon provide a perfect habitat for these surface bacteria. When detector proteins on the surface of the paneth cells detect the presence of surface bacteria, the paneth cells increase production of defensin which help regulate the number of surface bacteria in the crevice. In Crohn’s patients paneth cells exhibit an overproduction of definsins because a mutation has interfered with the proteins involved in the regulation of definsin production. Our research uses PCR to detect a mutation on CARD15 (R702W) that could cause this to occur.